OBV (On Balance Volume)
OBV (On Balance Volume) is a volume oscillator. It was developed by Joe Granville and introduced in his book Granville's New Key to Stock Market Profits in 1963.
Originally the oscillator was intended for stock market technical analysis, but nowadays it is widely used in forex trading as well.
With the help of OBV, traders can monitor an instrument's cumulative tick volume. According to Granville, volume always foreruns and influences price changes. The greater the volume is, the faster an
instrument's
price changes, and the faster it changes, the stronger its trend is. Thus, traders can see a price trend's presence and direction, evaluate its strength, and anticipate possible trend reversals and make
informed
trading decisions.
For these purposes, every period's tick volume, provided by the trading server together with price data, is assessed as positive or negative depending on whether the period's closing price is higher
(positive
volume) or lower (negative volume) than the closing price of the immediately preceding period. A positive volume is added to and a negative one is deducted from the cumulative volume of the preceding periods.
If the period's volume is neutral (stays unchanged), no action is taken. As a result, a running total of positive and negative values is obtained for each period.
On a chart, OBV is drawn in the form of a
line
moving up and down within the chart's area. The absolute value of OBV is not important, whereas, its line plays the major role in the oscillator's interpretation. The OBV line rises when positive volumes
prevail over negative ones and falls when negative volumes are stronger. A rising OBV reflects positive volume pressure that can lead to higher prices. Conversely, falling OBV reflects negative volume pressure
that can foreshadow lower prices. Thus, when the line goes up, it confirms an uptrend presence. Conversely, when the line goes down, a downtrend is confirmed. The line moving horizontally for a noticeable period
of time confirms a sideways market presence. The steeper the line is, the stronger the trend is. When divergences occur (read later), trend reversals can be expected.
As all oscillators, OBV is always drawn in an additional area below the market price chart.
On the following picture, you can see an example of OBV drawn in an additional area below the market price chart.
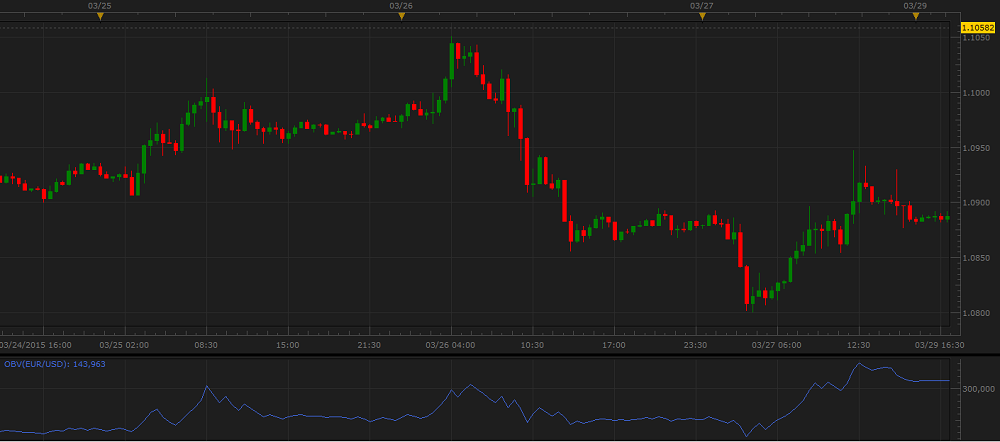
Thus, OBV is one of the few technical analysis tools that can serve as a leading indicator forecasting price changes before they take place.
OBV is not often used as a stand-alone oscillator. It works best in conjunction with a market price chart and some other indicators as a confirmation or denial tool of their trading signals.
To apply an OBV oscillator to a chart, a trader needs to follow the procedure common to all Marketscope indicators. For more information, see the Add Indicator article.
During the procedure, a trader can customize the oscillator by specifying its parameters in the Properties dialog box. For more information, see the Change Indicator Properties
article.
Please note that the oscillator lacks the Calculation parameters. Therefore, the Parameters tab of the OBV Properties dialog box contains only Style and Appearance headings.
When an OBV oscillator is drawn on a chart, a trader can analyze its information and try to interpret it correctly. The oscillator produces no direct trading signals, but its line's behavior can confirm other
indicators' information:
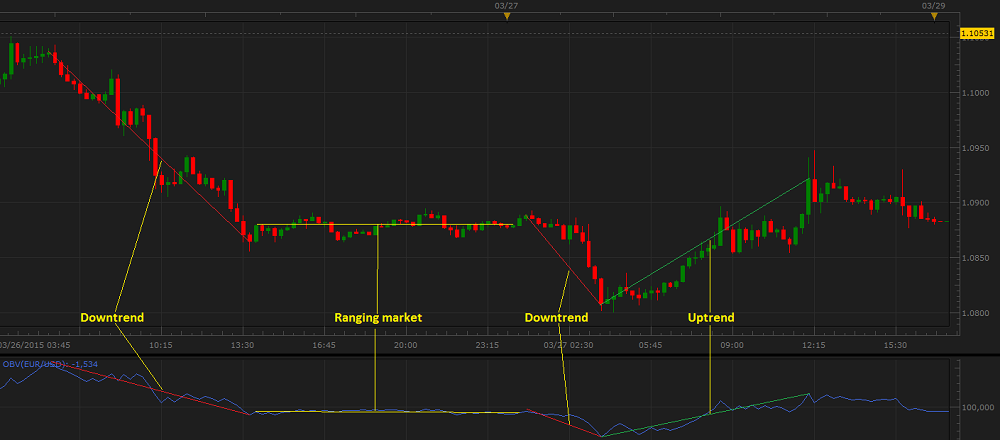
- Trend Confirmation
In the majority of cases, the OBV line's direction can be used to confirm a price trend presence and direction. When the OBV line moves step-for-step with an instrument's price, it confirms the direction
and strength of the instrument's price trend.
On the following picture, you can see examples of the oscillator's confirming different price trends.
- Trend Reversal Confirmation
To confirm an instrument's price trend reversal, look for a divergence. Divergences occur when the market price and the oscillator line move in the opposite directions (divergence itself) or towards
each other (often called convergence). Please remember that assessment of whether a period's volume is positive, negative, or neutral is based on closing prices, therefore, closing prices should be
considered when looking for divergences.
Divergences are subdivided into the following two types:
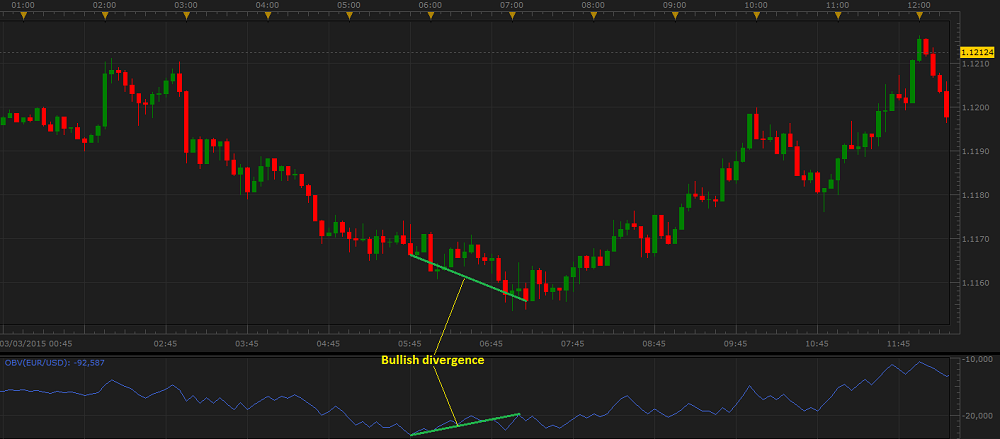
- Bullish divergence occurs when an instrument's price moves down, but the OBV line moves up or flat. This indicates that though the instrument's price declines, the growing volume pushes it up,
and the price trend will sooner or later reverse and start to rise.
On the following picture, you can see an example of a bullish divergence.
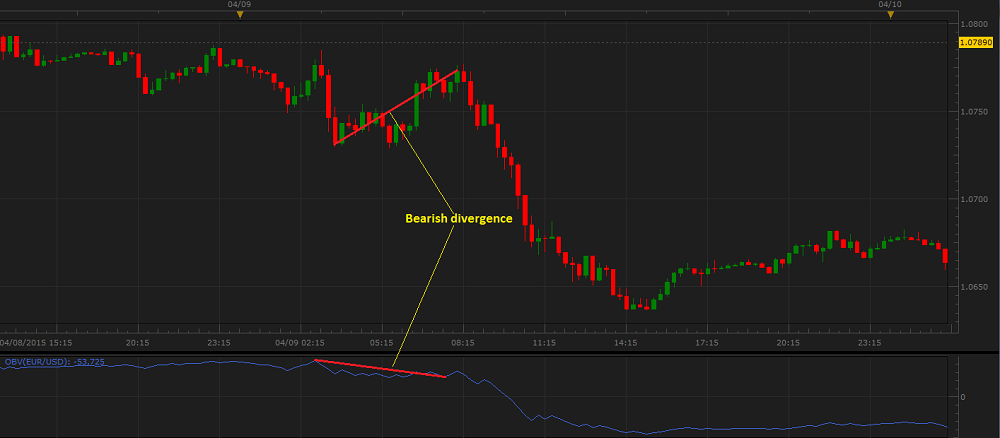
- Bearish divergence occurs when an instrument's price moves up, but the OBV line moves down or flat. This indicates that though the instrument's price rises, it has not enough volume to sustain
the growth, and the price trend will sooner or later reverse and start to decline.
On the following picture, you can see an example of a bearish divergence.
Please note that divergences are often misleading in a strong price trend: a bullish (or bearish) divergence can occur in a strong downtrend (or uptrend) and yet the strong downtrend (or uptrend) continues.
The OBV oscillator's values are calculated automatically using the following formulas:
If the current period's closing price is greater than that of the immediately preceding one (positive volume):
OBVi = OBVi-1 + TVi
If the current period's closing price is less than that of the immediately preceding one (negative volume):
OBVi = OBVi-1 - TVi
If the current period's closing price is equal to that of the immediately preceding one (neutral volume):
OBVi = OBVi-1
where:
OBVi - is the OBV value of the current period.
OBVi-1 - is the OBV value of the period immediately preceding the one being calculated.
TVi - is the tick volume of the current period.
back



